Social Stories and Autism
Developed by Carol Gray in 1990, Social Stories™ support preventative, or antecedent, strategies to help a child with autism successfully navigate challenging social settings. Social stories increase positive social behaviors and decrease challenging behaviors.
Structured routines and visual cues, among other transition strategies, help children with autism anticipate and respond well to changes in their environment. Social stories complement those interventions and help children with autism develop an understanding of the perspectives, emotions, and behaviors of themselves and others in specific settings.
At LeafWing Center, social stories may be integrated into our treatment approach depending on the needs of the child. Our therapists are experts in ABA therapy, proven to help children with autism. In this article, we will explain:
- What are Social Stories?
- Goals of Social Stories
- Benefits of Social Stories
- Components of Social Stories
- How to Write and Implement Social Stories

What Are Social Stories?
As defined by the concept’s author, Carol Gray, social stories are a “social learning tool that supports the safe and meaningful exchange of information between parents, professionals, and people with autism of all ages.”
Implementing the use of social stories in the classroom is a strategy that is likely not new to teachers. However, not all teachers know that they can be used to working with and teaching individuals with autism-specific skills surrounding social and behavioral needs.
In practice, social stories are characterized as follows:
- Short: A social story is a mini book that describes a social situation and the appropriate social responses.
- Specific: A social story teaches a specific desired response.
- Individualized: A social story uses descriptive, encouraging, and positive language, details, and illustrations that:
- Allow the child to see themselves and the people in their life reflected in the characters and dialogue.
- Use the first-person point of view or the child’s point of view as well as present or future verb tense.
- Answer questions the individual with autism may need to know to interact well with others (the who, what, when, where, and why in specific social situations).
- Consider the child’s level of vocabulary and comprehension, attention span, learning style, and personal interests.
At LeafWing, our personalized approach lets us get to know the children and families we support well. We have many resources available for parents and caregivers of children with autism.
Goals of Social Stories
Research shows that individuals with autism benefit greatly from the use of social stories and that benefits increase when the social story development process begins with clear goal setting. The goals of social stories center on the perspective of the child with autism, which helps maintain a positive and encouraging tone. In addition, they reflect the inputs of the entire care team, leading to greater skill or behavior generalization.
- Developing Skills for self-care, the classroom setting, and future work environments helps the individual work toward achieving targeted levels of independence.
- Teaching Social Norms provides a blueprint to help the child with autism interact with the world around them.
- Improving Sequencing gives children with autism the tools to move more easily from one task to another or from one environment to the next.
- Addressing Negative Behavior keeps the child with autism and others around them safe.
- Coping with Change in daily routine through social story interventions makes the unfamiliar feel more familiar.
- Celebrating the child’s strengths and recent “wins” through a social story builds their confidence and increases their openness to new skills and experiences.
Benefits of Social Stories
The benefits of social story interventions are well documented. When constructed and implemented according to certain guidelines, they have been shown to help children with autism:
- Increase shared understanding and empathy
- Build confidence
- Reduce anxiety
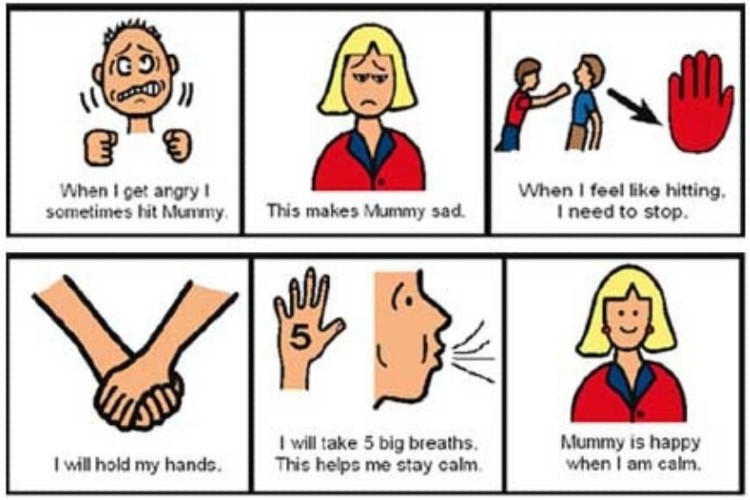
Components of Social Stories
Social stories are written using four sentence types. They are customary to include two to five descriptive, perspective, or control sentences.
- Descriptive Sentences: Provide information about the subject, setting, and action.
- Directive Sentences: Describe the appropriate behavioral responses.
- Perspective Sentences: Identify the possible feelings and reactions of others.
- Control Sentences: Describe the actions and responses of the story participants.
A note on control sentences: For example, a control sentence might be, “A puppy barks to get its owner’s attention.” Or, “Ginny yelled to get the teacher’s attention.” Writing social stories for students who have the tendency to over-focus on a specific part of the story may require omitting the control sentence.
How to Write Social Stories
When creating a social story, there are ten steps to follow:
- Identify the target situation or concept.
- Define the target behavior or skill.
- Collect baseline data on the target behavior.
- Write a social story using the four-sentence types.
- Present one to three sentences on each page.
- Use photographs and drawings or icons.
- Read the social story to the child/student and model the desired behavior for them.
- Collect data on the target behavior.
- Review the data and the social story procedures and modify them if they are ineffective.
- Plan for maintenance and generalization.
Social stories can be revisited as often as necessary, depending on the child’s receptiveness. Patience is key to the process.
Children with autism frequently do not maintain or generalize skills they have learned. Having a plan for maintenance and generalization helps improve the likelihood they will hold onto newly acquired skills. LeafWing therapists and caregivers will ultimately fade the use of a social story and plan activities to assist the student in generalizing skills across content, persons, environment, and situation.
Related Glossary Terms
Other Related Articles
- Strategies for autism in the classroom
- Supporting students with autism in the classroom with an assignment notebook
- Transition strategies for autistic students
- Autism communication strategies
Frequently asked questions about ABA therapy
What is ABA Therapy used for?
ABA-based therapy can be used in a multitude of areas. Currently, these interventions are used primarily with individuals living with ASD; however, their applications can be used with individuals living with pervasive developmental disorders as well as other disorders. For ASD, it can be used in effectively teaching specific skills that may not be in a child’s repertoire of skills to help him/her function better in their environment whether that be at home, school, or out in the community. In conjunction with skill acquisition programs, ABA-based interventions can also be used in addressing behavioral excesses (e.g., tantrum behaviors, aggressive behaviors, self-injurious behaviors). Lastly, it can also be utilized in parent/caregiver training.
In skill acquisition programs, a child’s repertoire of skills is assessed in the beginning phase of the services in key adaptive areas such as communication/language, self-help, social skills, and motor skills as well. Once skills to be taught are identified, a goal for each skill is developed and then addressed/taught by using ABA-based techniques to teach those important skills. Ultimately, an ABA-based therapy will facilitate a degree of maintenance (i.e., the child can still perform the learned behaviors in the absence of training/intervention over time) and generalization (i.e., the learned behaviors are observed to occur in situations different from the instructional setting). These two concepts are very important in any ABA-based intervention.
In behavior management, the challenging behaviors are assessed for their function in the beginning phase of the services. In this phase, the “why does this behavior happen in the first place?” is determined. Once known, an ABA-based therapy will be developed to not just decrease the occurrence of the behavior being addressed, but also teach the child a functionally-equivalent behavior that is socially-appropriate. For example, if a child resorts to tantrum behaviors when she is told she cannot have a specific item, she may be taught to accept an alternative or find an alternative for herself. Of course, we can only do this up to a certain point—the offering of alternatives. There comes a point when a ‘no’ means ‘no’ so the tantrum behavior will be left to run its course (i.e., to continue until it ceases). This is never easy and will take some time for parents/caregivers to get used to, but research has shown that over time and consistent application of an ABA-based behavior management program, the challenging behavior will get better.
In parent training, individuals that provide care for a child may receive customized “curriculum” that best fit their situation. A typical area covered in parent training is teaching responsible adults pertinent ABA-based concepts to help adults understand the rationale behind interventions that are being used in their child’s ABA-based services. Another area covered in parent training is teaching adults specific skill acquisition programs and/or behavior management programs that they will implement during family time. Other areas covered in parent training may be data collection, how to facilitate maintenance, how to facilitate generalization of learned skills to name a few.
There is no “one format” that will fit all children and their families’ needs. The ABA professionals you’re currently working with, with your participation, will develop an ABA-based treatment package that will best fit your child’s and your family’s needs. For more information regarding this topic, we encourage you to speak with your BCBA or reach out to us at info@leafwingcenter.org.
Who Can Benefit From ABA Therapy?
There is a common misconception that the principles of ABA are specific to Autism. This is not the case. The principles and methods of ABA are scientifically backed and can be applied to any individual. With that said, the U.S. Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association consider ABA to be an evidence based practice. Forty years of extensive literature have documented ABA therapy as an effective and successful practice to reduce problem behavior and increase skills for individuals with intellectual disabilities and Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Children, teenagers, and adults with ASD can benefit from ABA therapy. Especially when started early, ABA therapy can benefit individuals by targeting challenging behaviors, attention skills, play skills, communication, motor, social, and other skills. Individuals with other developmental challenges such as ADHD or intellectual disability can benefit from ABA therapy as well. While early intervention has been demonstrated to lead to more significant treatment outcomes, there is no specific age at which ABA therapy ceases to be helpful.
Additionally, parents and caregivers of individuals living with ASD can also benefit from the principles of ABA. Depending on the needs of your loved one, the use of specified ABA techniques in addition to 1:1 services, may help produce more desirable treatment outcomes. The term “caregiver training” is common in ABA services and refers to the individualized instruction that a BCBA or ABA Supervisor provides to parents and caregivers. This typically involves a combination of individualized ABA techniques and methods parents and caregivers can use outside of 1:1 sessions to facilitate ongoing progress in specified areas.
ABA therapy can help people living with ASD, intellectual disability, and other developmental challenges achieve their goals and live higher quality lives.
What does ABA Therapy look like?
Agencies that provide ABA-based services in the home-setting are more likely to implement ABA services similarly than doing the same exact protocols or procedures. Regardless, an ABA agency under the guidance of a Board-Certified Behavior Analyst follows the same research-based theories to guide treatment that all other acceptable ABA agencies use.
ABA-based services start with a functional behavior assessment (FBA). In a nutshell, a FBA assesses why the behaviors may be happening in the first place. From there, the FBA will also determine the best way to address the difficulties using tactics that have been proven effective over time with a focus on behavioral replacement versus simple elimination of a problem behavior. The FBA will also have recommendations for other relevant skills/behaviors to be taught and parent skills that can be taught in a parent training format to name a few. From there, the intensity of the ABA-based services is determined, again, based on the clinical needs of your child. The completed FBA is then submitted to the funding source for approval.
One-on-one sessions between a behavior technician and your child will start once services are approved. The duration per session and the frequency of these sessions per week/month will all depend on how many hours your child’s ABA services have been approved for—usually, this will be the number recommended in the FBA. The sessions are used to teach identified skills/behaviors via effective teaching procedures. Another aspect of ABA-based services in the home-setting is parent training. Parent training can take many forms depending on what goals have been established during the FBA process. The number of hours dedicated for parent training is also variable and solely depends on the clinical need for it. If a 1:1 session is between a behavior technician and your child, a parent training session or appointment is between you and the case supervisor and with and without your child present, depending on the parent goal(s) identified. Parent training service’s goal is for you to be able to have ample skills/knowledge in order for you to become more effective in addressing behavioral difficulties as they occur outside of scheduled ABA sessions. Depending on the goals established, you may be required to participate in your child’s 1:1 sessions. These participations are a good way for you to practice what you have learned from the case supervisor while at the same time, having the behavior technician available to you to give you feedback as you practice on those new skills.
As mentioned in the beginning, no two ABA agencies will do the same exact thing when it comes to providing ABA services; however, good agencies will always base their practice on the same empirically-proven procedures.
How do I start ABA Therapy?
In most cases, the first item required to start ABA therapy is the individual’s autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis report. This is typically conducted by a doctor such as a psychiatrist, psychologist, or a developmental pediatrician. Most ABA therapy agencies and insurance companies will ask for a copy of this diagnosis report during the intake process as it is required to request an ABA assessment authorization from the individual’s medical insurance provider.
The second item required to start ABA therapy is a funding source. In the United States, and in cases where Medi-Cal or Medicare insurances are involved, there is a legal requirement for ABA services to be covered when there is a medical necessity (ASD diagnosis). Medi-Cal and Medicare cover all medically necessary behavioral health treatment services for beneficiaries. This typically includes children diagnosed with ASD. Since Applied Behavior Analysis is an evidence based and effective treatment for individuals with ASD, it is considered a covered treatment when medically necessary. In many cases, private insurance will also cover ABA services when medically necessary, however in these cases, it is best to speak directly with your medical insurance provider to determine the specifics of the coverage and to ensure that ABA is in fact, a covered benefit. Additionally, some families opt to pay for ABA services out-of-pocket.
The next step to starting ABA therapy is to contact an ABA provider whom you are interested in working with. Depending on your geographic location, ABA agencies exist in many cities across the United States. Your insurance carrier, local support groups, and even a thorough online search can help you find reputable and properly credentialed ABA agencies near you. Our organization, LeafWing Center, is based in southern California and is recognized for aiding people with ASD achieve their goals with the research based on applied behavior analysis.
Once you have identified the ABA provider with whom you wish to work, they should help you facilitate the next steps. These will include facilitating paperwork and authorizations with your funding source. Once the assessment process begins, a BCBA (Board Certified Behavior Analyst) or qualified Program Supervisor should get in contact with you to arrange times in which interviews with parents/caregivers and observations of your loved one can be conducted. This will help in the process of gathering important clinical information so that with your collaboration, the most effective treatment plans and goals can be established for your loved one. This process is referred to as the Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) and is elaborated on in different blog posts on our website. With regard as to what can be expected once ABA therapy begins, please read our blog post titled: When You Start an ABA program, What Should You Reasonably Expect from Your Service Provider?































