Autism and Motivation in Children
Autism and motivation in children can be a challenging combination. Motivation can be difficult for many people. Plenty of us struggle to exercise regularly or eat well. This is true even though these lifestyle changes could likely make a large difference in our health and, consequently, our quality of life. Motivating children with autism also requires empathy and patience.
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are not always motivated to master basic tasks or life skills in the same ways as neurotypical children. Autism and motivation in children can seem incompatible. Or, perhaps your child is highly motivated to hyper-focus on certain tasks, just not the tasks you’d like them to choose. Motivating children with autism can be a struggle until you identify the specific factors that inspire your child.
Table of Contents
- Intrinsic Motivation And Autism
- Autism And Motivation
- Intrinsic Motivation And Extrinsic Motivation Techniques
- Motivating Children With Autism

Each child with ASD may be motivated by different:
- activities
- environments
- people
- rewards
- perceptions
It is important to spend time learning what is motivating to your autistic child. Then, you can practice applying this information to help your child grow in their own motivation.
Intrinsic Motivation and Autism
In Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) we sometimes discuss motivation by categorizing it in two ways—intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation refers to motivation that would be described as coming from within a person. That is, you do something because you like it.
For example, the prima ballerina rehearses 8 hours a day because she wants to be able to perform exceptionally. Autism and motivation in children can show up as an inner drive to accomplish a task or observe an activity. Your child may love cars, and they are highly internally motivated to sit by a window and watch traffic drive by or play with their own toy cars for hours.
Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, refers to motivation that comes from others or our environment. For example, some employees in a manufacturing company may show up to work on time to avoid getting in trouble with the boss. Children with ASD may be motivated to put away toys with the reward of their favorite snack or TV show.
Behavior is affected by many influences. Autism and motivation both influence behavior. By observing patterns in your child’s choices, you can learn the best ways to encourage them to grow and learn new habits.
Autism and Motivation
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivational mechanisms apply to children living with ASD. Many children with autism are not interested in doing all of the things that we would like them to do. Motivating children with ASD to accomplish tasks or master skills is frequently different from motivating neurotypical children.
Some of our children on the spectrum may choose to engage in repetitive play or ignore others. Autism and motivation in children may look like your child only engaging in things that they find interesting. When this free time is interrupted, or when they are asked to move their attention to something or someone else, they may suddenly appear unmotivated to learn or disinterested. In some cases, other challenging behaviors can occur if we follow through with our demands.
Factors that influence autism and motivation can be observed in your child. If you find your child happily engaging in an activity, take note of the type of activity and the environment. Certain types of play, food or stimuli may be preferred. For example, your child may really enjoy playing with marbles. It may be helpful to ask the following questions to determine what is motivating children with autism. Does your child:
- Suddenly, stop enjoying or engaging with this activity if there is noise or music in the background.
- Enjoy this activity more when they have different paths and features for the marbles to follow.
- Do they like to play with marbles independently of peers, or do they enjoy others joining them?
Environmental inputs can influence children with ASD so strongly that motivation is impacted. An autistic child’s sensitivities are key factors in determining how autism and motivation should be approached to achieve the most effective outcomes.

Motivating Autistic Children: Intrinsic Motivation and Extrinsic Motivation Techniques
Without motivation, the learning process may be significantly slowed down or made to feel impossible. For this reason, every effort is made to increase a child’s motivation to learn at every stage of an ABA program. Ample time is spent finding out what things a child likes. Therapists will use reinforcer surveying or reinforcer sampling to determine the things that will motivate your autistic child long enough to learn. It is also important to learn what is not motivating to your child so that you can avoid those challenges.
Motivation in an intensive Applied Behavior Analysis program may initially take the form of something extrinsic, such as being rewarded with their favorite foods, candies, or activities. Frequently, verbal praise and high-fives or anything that a child may find enjoyable can be used for positive reinforcement.
However, it is hoped that over time, this motivation will transition from extrinsic to intrinsic such that a child will engage in learning for personal joy and accomplishment. For example, a child may be motivated to build a block house because they look forward to feeling happy with the completed structure. To lead to this intrinsic motivation, rewards like candy or other foods can be systematically reduced while more internal, natural rewards take their place.

Motivating Children With Autism
Motivating children with autism is a multiple-step process.
- Identify what your child enjoys on their own or is already intrinsically motivated to engage with or accomplish.
- Select rewards and positive reinforcements for your child to use as extrinsic motivation.
- Gradually reduce the extrinsic rewards as you notice your child learning a positive habit or experiencing more positive feelings about accomplishing activities.
- Communicate with your child about the changes they are experiencing. Motivating children with autism gains momentum as your child feels supported and acknowledges their own positive progress.
Using extrinsic rewards is a common concern that others may have when considering ABA therapy. However, professionals leading ABA programs plan and strive to transition from extrinsic into more intrinsic forms of reinforcers over time. Using transitional positive reinforcements, or extrinsic rewards, is an important factor in a child’s program that creates more positive associations with new behaviors.
If you are struggling to identify what motivates your autistic child or you would like to see changes in what motivates your child, it may be a good time to reach out to a trained professional. You can get help evaluating the influences of autism and motivation in your child. An ABA professional can also create a program tailored to your child to help them make progress toward motivational goals.
Related Glossary Terms
Other Related Articles
- When Is A Good Time To Start ABA Therapy?
- ABA Therapy At Home
- How To Use Visuals To Help Students With Autism
- Supporting Students With Autism In The Classroom With An Assignment Notebook
Frequently asked questions about ABA therapy
What is ABA Therapy used for?
ABA-based therapy can be used in a multitude of areas. Currently, these interventions are used primarily with individuals living with ASD; however, their applications can be used with individuals living with pervasive developmental disorders as well as other disorders. For ASD, it can be used in effectively teaching specific skills that may not be in a child’s repertoire of skills to help him/her function better in their environment whether that be at home, school, or out in the community. In conjunction with skill acquisition programs, ABA-based interventions can also be used in addressing behavioral excesses (e.g., tantrum behaviors, aggressive behaviors, self-injurious behaviors). Lastly, it can also be utilized in parent/caregiver training.
In skill acquisition programs, a child’s repertoire of skills is assessed in the beginning phase of the services in key adaptive areas such as communication/language, self-help, social skills, and motor skills as well. Once skills to be taught are identified, a goal for each skill is developed and then addressed/taught by using ABA-based techniques to teach those important skills. Ultimately, an ABA-based therapy will facilitate a degree of maintenance (i.e., the child can still perform the learned behaviors in the absence of training/intervention over time) and generalization (i.e., the learned behaviors are observed to occur in situations different from the instructional setting). These two concepts are very important in any ABA-based intervention.
In behavior management, the challenging behaviors are assessed for their function in the beginning phase of the services. In this phase, the “why does this behavior happen in the first place?” is determined. Once known, an ABA-based therapy will be developed to not just decrease the occurrence of the behavior being addressed, but also teach the child a functionally-equivalent behavior that is socially-appropriate. For example, if a child resorts to tantrum behaviors when she is told she cannot have a specific item, she may be taught to accept an alternative or find an alternative for herself. Of course, we can only do this up to a certain point—the offering of alternatives. There comes a point when a ‘no’ means ‘no’ so the tantrum behavior will be left to run its course (i.e., to continue until it ceases). This is never easy and will take some time for parents/caregivers to get used to, but research has shown that over time and consistent application of an ABA-based behavior management program, the challenging behavior will get better.
In parent training, individuals that provide care for a child may receive customized “curriculum” that best fit their situation. A typical area covered in parent training is teaching responsible adults pertinent ABA-based concepts to help adults understand the rationale behind interventions that are being used in their child’s ABA-based services. Another area covered in parent training is teaching adults specific skill acquisition programs and/or behavior management programs that they will implement during family time. Other areas covered in parent training may be data collection, how to facilitate maintenance, how to facilitate generalization of learned skills to name a few.
There is no “one format” that will fit all children and their families’ needs. The ABA professionals you’re currently working with, with your participation, will develop an ABA-based treatment package that will best fit your child’s and your family’s needs. For more information regarding this topic, we encourage you to speak with your BCBA or reach out to us at info@leafwingcenter.org.
Who Can Benefit From ABA Therapy?
There is a common misconception that the principles of ABA are specific to Autism. This is not the case. The principles and methods of ABA are scientifically backed and can be applied to any individual. With that said, the U.S. Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association consider ABA to be an evidence based practice. Forty years of extensive literature have documented ABA therapy as an effective and successful practice to reduce problem behavior and increase skills for individuals with intellectual disabilities and Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Children, teenagers, and adults with ASD can benefit from ABA therapy. Especially when started early, ABA therapy can benefit individuals by targeting challenging behaviors, attention skills, play skills, communication, motor, social, and other skills. Individuals with other developmental challenges such as ADHD or intellectual disability can benefit from ABA therapy as well. While early intervention has been demonstrated to lead to more significant treatment outcomes, there is no specific age at which ABA therapy ceases to be helpful.
Additionally, parents and caregivers of individuals living with ASD can also benefit from the principles of ABA. Depending on the needs of your loved one, the use of specified ABA techniques in addition to 1:1 services, may help produce more desirable treatment outcomes. The term “caregiver training” is common in ABA services and refers to the individualized instruction that a BCBA or ABA Supervisor provides to parents and caregivers. This typically involves a combination of individualized ABA techniques and methods parents and caregivers can use outside of 1:1 sessions to facilitate ongoing progress in specified areas.
ABA therapy can help people living with ASD, intellectual disability, and other developmental challenges achieve their goals and live higher quality lives.
What does ABA Therapy look like?
Agencies that provide ABA-based services in the home-setting are more likely to implement ABA services similarly than doing the same exact protocols or procedures. Regardless, an ABA agency under the guidance of a Board-Certified Behavior Analyst follows the same research-based theories to guide treatment that all other acceptable ABA agencies use.
ABA-based services start with a functional behavior assessment (FBA). In a nutshell, a FBA assesses why the behaviors may be happening in the first place. From there, the FBA will also determine the best way to address the difficulties using tactics that have been proven effective over time with a focus on behavioral replacement versus simple elimination of a problem behavior. The FBA will also have recommendations for other relevant skills/behaviors to be taught and parent skills that can be taught in a parent training format to name a few. From there, the intensity of the ABA-based services is determined, again, based on the clinical needs of your child. The completed FBA is then submitted to the funding source for approval.
One-on-one sessions between a behavior technician and your child will start once services are approved. The duration per session and the frequency of these sessions per week/month will all depend on how many hours your child’s ABA services have been approved for—usually, this will be the number recommended in the FBA. The sessions are used to teach identified skills/behaviors via effective teaching procedures. Another aspect of ABA-based services in the home-setting is parent training. Parent training can take many forms depending on what goals have been established during the FBA process. The number of hours dedicated for parent training is also variable and solely depends on the clinical need for it. If a 1:1 session is between a behavior technician and your child, a parent training session or appointment is between you and the case supervisor and with and without your child present, depending on the parent goal(s) identified. Parent training service’s goal is for you to be able to have ample skills/knowledge in order for you to become more effective in addressing behavioral difficulties as they occur outside of scheduled ABA sessions. Depending on the goals established, you may be required to participate in your child’s 1:1 sessions. These participations are a good way for you to practice what you have learned from the case supervisor while at the same time, having the behavior technician available to you to give you feedback as you practice on those new skills.
As mentioned in the beginning, no two ABA agencies will do the same exact thing when it comes to providing ABA services; however, good agencies will always base their practice on the same empirically-proven procedures.
How do I start ABA Therapy?
In most cases, the first item required to start ABA therapy is the individual’s autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis report. This is typically conducted by a doctor such as a psychiatrist, psychologist, or a developmental pediatrician. Most ABA therapy agencies and insurance companies will ask for a copy of this diagnosis report during the intake process as it is required to request an ABA assessment authorization from the individual’s medical insurance provider.
The second item required to start ABA therapy is a funding source. In the United States, and in cases where Medi-Cal or Medicare insurances are involved, there is a legal requirement for ABA services to be covered when there is a medical necessity (ASD diagnosis). Medi-Cal and Medicare cover all medically necessary behavioral health treatment services for beneficiaries. This typically includes children diagnosed with ASD. Since Applied Behavior Analysis is an evidence based and effective treatment for individuals with ASD, it is considered a covered treatment when medically necessary. In many cases, private insurance will also cover ABA services when medically necessary, however in these cases, it is best to speak directly with your medical insurance provider to determine the specifics of the coverage and to ensure that ABA is in fact, a covered benefit. Additionally, some families opt to pay for ABA services out-of-pocket.
The next step to starting ABA therapy is to contact an ABA provider whom you are interested in working with. Depending on your geographic location, ABA agencies exist in many cities across the United States. Your insurance carrier, local support groups, and even a thorough online search can help you find reputable and properly credentialed ABA agencies near you. Our organization, LeafWing Center, is based in southern California and is recognized for aiding people with ASD achieve their goals with the research based on applied behavior analysis.
Once you have identified the ABA provider with whom you wish to work, they should help you facilitate the next steps. These will include facilitating paperwork and authorizations with your funding source. Once the assessment process begins, a BCBA (Board Certified Behavior Analyst) or qualified Program Supervisor should get in contact with you to arrange times in which interviews with parents/caregivers and observations of your loved one can be conducted. This will help in the process of gathering important clinical information so that with your collaboration, the most effective treatment plans and goals can be established for your loved one. This process is referred to as the Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) and is elaborated on in different blog posts on our website. With regard as to what can be expected once ABA therapy begins, please read our blog post titled: When You Start an ABA program, What Should You Reasonably Expect from Your Service Provider?



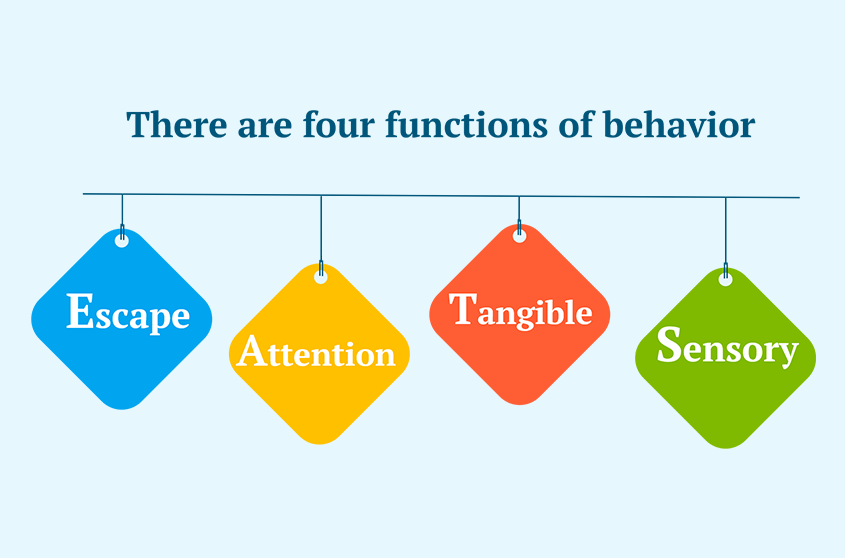














 The following are things that you should expect as a parent when you begin treatment for your child with Autism.
The following are things that you should expect as a parent when you begin treatment for your child with Autism.




 An effective ABA program should have the following components:
An effective ABA program should have the following components: